算法解释
这里我们引用一下维基百科的描述:“动态规划(Dynamic Programming, DP)在查找有很多重叠子问题的情况的最优解时有效。它将题重新组合成子问题。为了避免多次解决这些子问题,它们的结果都逐渐被计算并被保存,从简单的问题直到整个问题都被解决。因此,动态规划保存递归时的结果,因而不会在解决同样的问题时花费时间······动态规划只能应用于有最优子结构的问题。最优子结构的意思是局部最优解能决定全局最优解(对有些问题这个要求并不能完全满足,故有时需要引入一定的近似)。简单地说,问题能够分解成子问题来解决。”
通俗一点来讲,动态规划和其它遍历算法(如深/广度优先搜索)都是将原问题拆成多个子问题然后求解,他们之间最本质的区别是,动态规划保存子问题的解,避免重复计算。解决动态规划问题的关键是找到状态转移方程,这样我们可以通过计算和储存子问题的解来求解最终问题。
同时,我们也可以对动态规划进行空间压缩,起到节省空间消耗的效果。这一技巧笔者将在之后的题目中介绍。
在一些情况下,动态规划可以看成是带有状态记录(memoization)的优先搜索。状态记录的意思为,如果一个子问题在优先搜索时已经计算过一次,我们可以把它的结果储存下来,之后遍历到该子问题的时候可以直接返回储存的结果。动态规划是自下而上的,即先解决子问题,再解决父问题;而用带有状态记录的优先搜索是自上而下的,即从父问题搜索到子问题,若重复搜索到同一个子问题则进行状态记录,防止重复计算。如果题目需求的是最终状态,那么使用动态搜索比较方便;如果题目需要输出所有的路径,那么使用带有状态记录的优先搜索会比较方便。
一维动态规划
LeetCode NO.70 Climbing Stairs
题目描述
You are climbing a staircase. It takes n steps to reach the top.
Each time you can either climb 1 or 2 steps. In how many distinct ways can you climb to the top?
Example 1:
Input: n = 2
Output: 2
Explanation: There are two ways to climb to the top.
1 step + 1 step
2 steps
Example 2:- Input: n = 3
Output: 3
题解
经典爬楼梯问题,定义一个数组dp,dp[i] 表示走到第i 阶的方法数。因为我们每次可以走一步或者两步,所以第i 阶可以从第i-1 或i-2 到达。换句话说,走到第i 阶的方法数即为走到第i-1 阶的方法数加上走到第i-2 阶的方法数。这样我们就得到了状态转移方程dp[i] = dp[i-1] + dp[i-2]。注意边界条件的处理。
1 | int climbStairs(int n) { |
我们可以压缩空间,只保留当前节点的前两个节点值。
1 | int climbStairs(int n) { |
LeetCode NO.198 House Robber
题目描述
You are a professional robber planning to rob houses along a street. Each house has a certain amount of money stashed, the only constraint stopping you from robbing each of them is that adjacent houses have security systems connected and it will automatically contact the police if two adjacent houses were broken into on the same night.
Given an integer array nums representing the amount of money of each house, return the maximum amount of money you can rob tonight without alerting the police.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,1]
Output: 4
Explanation: Rob house 1 (money = 1) and then rob house 3 (money = 3).
Total amount you can rob = 1 + 3 = 4.
Example 2:Input: nums = [2,7,9,3,1]
Output: 12
Explanation: Rob house 1 (money = 2), rob house 3 (money = 9) and rob house 5 (money = 1).
Total amount you can rob = 2 + 9 + 1 = 12.Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 100
0 <= nums[i] <= 400
题解
定义一个数组dp,dp[i] 表示抢劫到第i 个房子时,可以抢劫的最大数量。我们考虑dp[i],此时可以抢劫的最大数量有两种可能,一种是我们选择不抢劫这个房子,此时累计的金额即为dp[i-1];另一种是我们选择抢劫这个房子,那么此前累计的最大金额只能是dp[i-2],因为我们不能够抢劫第i-1 个房子,否则会触发警报机关。因此本题的状态转移方程为dp[i] = max(dp[i-1],nums[i-1] + dp[i-2])。
1 | int rob(vector<int>& nums) { |
同样可以进行空间压缩。
1 | int rob(vector<int>& nums) { |
LeetCode NO.413 Arithmetic Slices
题目描述
An integer array is called arithmetic if it consists of at least three elements and if the difference between any two consecutive elements is the same.
For example, [1,3,5,7,9], [7,7,7,7], and [3,-1,-5,-9] are arithmetic sequences.
Given an integer array nums, return the number of arithmetic subarrays of nums.A subarray is a contiguous subsequence of the array.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4]
Output: 3
Explanation: We have 3 arithmetic slices in nums: [1, 2, 3], [2, 3, 4] and [1,2,3,4] itself.
Example 2:Input: nums = [1]
Output: 0Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 5000
-1000 <= nums[i] <= 1000
题解
这道题略微特殊,因为要求是等差数列,可以很自然的想到子数组必定满足num[i] - num[i-1]= num[i-1] - num[i-2]。然而由于我们对于dp 数组的定义通常为以i 结尾的,满足某些条件的子数组数量,而等差子数组可以在任意一个位置终结,因此此题在最后需要对dp 数组求和。
1 | int numberOfArithmeticSlices(vector<int>& nums) { |
二维动态规划
LeetCode NO.64 Minimum Path Sum
题目描述
Given a m x n grid filled with non-negative numbers, find a path from top left to bottom right, which minimizes the sum of all numbers along its path.
Note: You can only move either down or right at any point in time.
Example 1:
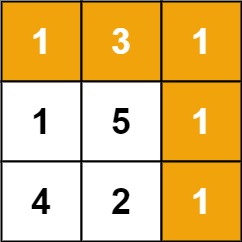
Input: grid = [[1,3,1],[1,5,1],[4,2,1]]
Output: 7
Explanation: Because the path 1 → 3 → 1 → 1 → 1 minimizes the sum.
Example 2:Input: grid = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]
Output: 12Constraints:
m == grid.length
n == grid[i].length
1 <= m, n <= 200
0 <= grid[i][j] <= 100
题解
我们可以定义一个同样是二维的dp 数组,其中dp[i][j] 表示从左上角开始到(i, j) 位置的最优路径的数字和。因为每次只能向下或者向右移动,我们可以很容易得到状态转移方程dp[i][j] =min(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]) + grid[i][j],其中grid 表示原数组。
1 | int minPathSum(vector<vector<int>>& grid) { |
由于dp[i][j]只与其上面和左面的邻居有关,可以只用一维数组保存结果,进行空间压缩。
1 | int minPathSum(vector<vector<int>>& grid) { |
LeetCode NO.542 01 Matrix
题目描述
Given a matrix consists of 0 and 1, find the distance of the nearest 0 for each cell.
The distance between two adjacent cells is 1.
Example 1:
Input:
[[0,0,0],
[0,1,0],
[0,0,0]]Output:
[[0,0,0],
[0,1,0],
[0,0,0]]
Example 2:Input:
[[0,0,0],
[0,1,0],
[1,1,1]]Output:
[[0,0,0],
[0,1,0],
[1,2,1]]Note:
The number of elements of the given matrix will not exceed 10,000.
There are at least one 0 in the given matrix.
The cells are adjacent in only four directions: up, down, left and right.
题解
一般来说,因为这道题涉及到四个方向上的最近搜索,所以很多人的第一反应可能会是广度优先搜索。但是对于一个大小O¹mnº 的二维数组,对每个位置进行四向搜索,最坏情况的时间复杂度(即全是1)会达到恐怖的O¹m2n2º。一种办法是使用一个dp 数组做memoization,使得广度优先搜索不会重复遍历相同位置;另一种更简单的方法是,我们从左上到右下进行一次动态搜索,再从右下到左上进行一次动态搜索。两次动态搜索即可完成四个方向上的查找。
1 | vector<vector<int>> updateMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) { |
LeetCode NO.221 Maximal Square
题目描述
Given an m x n binary matrix filled with 0’s and 1’s, find the largest square containing only 1’s and return its area.
Example 1:
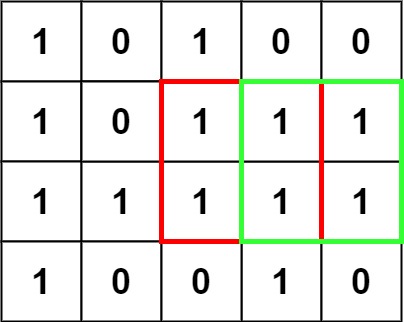
Input: matrix = [[“1”,”0”,”1”,”0”,”0”],[“1”,”0”,”1”,”1”,”1”],[“1”,”1”,”1”,”1”,”1”],[“1”,”0”,”0”,”1”,”0”]]
Output: 4Example 2:
Input: matrix = [[“0”,”1”],[“1”,”0”]]
Output: 1
题解
对于在矩阵内搜索正方形或长方形的题型,一种常见的做法是定义一个二维dp 数组,其中dp[i][j] 表示满足题目条件的、以(i, j) 为右下角的正方形或者长方形的属性。对于本题,则表示以(i, j) 为右下角的全由1 构成的最大正方形面积。如果当前位置是0,那么dp[i][j] 即为0;如果当前位置是1,我们假设dp[i][j] = $k^2$,其充分条件为dp[i-1][j-1]、dp[i][j-1] 和dp[i-1][j] 的值必须都不小于$(k-1)^2$,否则(i, j) 位置不可以构成一个边长为k 的正方形。同理,如果这三个值中的的最小值为k-1,则(i, j) 位置一定且最大可以构成一个边长为k的正方形。
1 | int maximalSquare(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) { |
分割类题型
LeetCode NO.279 Perfect Squares
题目描述
Given an integer n, return the least number of perfect square numbers that sum to n.
A perfect square is an integer that is the square of an integer; in other words, it is the product of some integer with itself. For example, 1, 4, 9, and 16 are perfect squares while 3 and 11 are not.
Example 1:
Input: n = 12
Output: 3
Explanation: 12 = 4 + 4 + 4.
Example 2:Input: n = 13
Output: 2
Explanation: 13 = 4 + 9.Constraints:
1 <= n <= 104
题解
对于分割类型题,动态规划的状态转移方程通常并不依赖相邻的位置,而是依赖于满足分割条件的位置。我们定义一个一维矩阵dp,其中dp[i] 表示数字i 最少可以由几个完全平方数相加构成。在本题中,位置i 只依赖$i - k^2$ 的位置,如$i - 1、i - 4、i - 9 $等等,才能满足完全平方分割的条件。因此dp[i] 可以取的最小值即为$1 + min(dp[i-1], dp[i-4], dp[i-9] ···)$。
1 | int numSquares(int n) { |
LeetCode NO.139 Word Break
题目描述
Given a string s and a dictionary of strings wordDict, return true if s can be segmented into a space-separated sequence of one or more dictionary words.
Note that the same word in the dictionary may be reused multiple times in the segmentation.
Example 1:
Input: s = “leetcode”, wordDict = [“leet”,”code”]
Output: true
Explanation: Return true because “leetcode” can be segmented as “leet code”.
Example 2:Input: s = “applepenapple”, wordDict = [“apple”,”pen”]
Output: true
Explanation: Return true because “applepenapple” can be segmented as “apple pen apple”.
Note that you are allowed to reuse a dictionary word.
Example 3:Input: s = “catsandog”, wordDict = [“cats”,”dog”,”sand”,”and”,”cat”]
Output: falseConstraints:
1 <= s.length <= 300
1 <= wordDict.length <= 1000
1 <= wordDict[i].length <= 20
s and wordDict[i] consist of only lowercase English letters.
All the strings of wordDict are unique.
题解
令dp[i]数组表示字符串(0,i)位置能够被分割成字典中出现的单词。
对于一个单词word,假设它的长度为len,dp[i]为true的条件是:
- dp[i-len]为true
- 子字符串(i-len,i)和单词word相同
上述是对于一个单词来说,dp[i]为true的条件,那么推广到一个字典wordDict,只要遍历整个字典,对每个单词做上述的分析判断即可。注意这里每次比对的结果应该是或的关系。
1 | bool wordBreak(string s, vector<string>& wordDict) { |